JSON information are generally used nowadays for sending information to functions. Be it an online software, an API, or a cellular software, JSON is utilized by virtually each crew as it’s light-weight and self-describing.
Attributable to its excessive recognition and vast utilization, it is very important perceive and know what JSON is, its options, its completely different information varieties, file codecs, and so on. On this weblog, we might be studying about JSON, its options, information varieties, and file codecs. We’ll then proceed to be taught to learn JSON information in Java utilizing the Google Gson library.
Desk of Contents
- What’s JSON?
- Options of JSON
- JSON Information Sorts
- JSON Syntax Guidelines
- Understanding the JSON file content material
- Methods to learn JSON information in Java utilizing the Google Gson library
What Is JSON?
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation and is an open-standard information interchange format identified for being self-describing and light-weight. It was derived from JavaScript and was initially specified by Douglas Crockford.
JSON is each straightforward to learn and write and can also be language-independent. It helps information constructions similar to arrays and objects, permitting for versatile information group. It’s broadly utilized by software program groups for storing and transporting information. It’s usually used when information is distributed from a server to net pages; the RESTful APIs use JSON information for sending and receiving information over HTTP.
Options of JSON
The next are a number of the key options of JSON.
- Easy and simple to grasp: JSON is self-describing which makes it easy and simple to learn and write. It helps in effectively transferring information over the web.
- Language unbiased: JSON makes use of a text-based format that may be parsed and simply used with a number of programming languages. This comparatively makes it a lot sooner than different text-based structured information.
- Help for complicated information varieties: JSON helps a number of information varieties together with
Strings,numbers,boolean,objects,arrays, andnull. - Interoperability: Since JSON originated from JavaScript, it integrates seamlessly with JavaScript-based functions, making it extremely appropriate for net improvement.
JSON Information Sorts
As simply listed, the next information varieties are supported by JSON:
StringQuantityBooleanObjectsArraysNull
JSON Syntax Guidelines
The next are essential syntax guidelines for JSON
- Information is in title/worth pairs.
- Information is separated by commas.
- Curly braces maintain objects.
- Sq. brackets maintain arrays.
- JSON doesn’t help feedback.
- The JSON file needs to be saved with the extension .json.
Understanding the JSON File Content material
There are a number of methods wherein the JSON file content material may be designed as follows:
- It may be an object that has an Array holding a number of objects.
- It may be an Array with a number of Objects.
- It could possibly solely be an Object.
- It may be an array with an Object holding one other array and so forth.
JSON Objects
Right here is an instance of a JSON file that has solely a JSON object as its content material.
{
"carname": "Ferrari",
"makeyear": 2024,
"engine": "F1V12",
"estimatedprice": "450K USD"
}The info is saved in a key/worth pair throughout the curly brackets “{ }” within the JSON object.
Named JSON Objects
JSON permits naming the JSON objects. This may be completed by naming the JSON object as proven within the instance under:
{
"workers": [
{
"id": "1",
"activeEmployee": true,
"designation": "Sr. Manager",
"bankdetails": {
"bankname": "Axis Bank Ltd",
"branch": "Mumbai",
"ifsc": "UTIV9089",
"accountno": 2646768
}
},
{
"id": "1",
"activeEmployee": true,
"designation": "Sr. Manager",
"bankdetails": {
"bankname": "Axis Bank Ltd",
"branch": "Mumbai",
"ifsc": "UTIV9089",
"accountno": 2646768
}
}
]
}
The above JSON file holds the worker particulars. The worker financial institution particulars are saved in a JSON object that’s named “bankdetails”. This can be known as the “bankdetails” key holding the worth for the main points of the financial institution.
"bankdetails": {
"bankname": "Axis Financial institution Ltd",
"department": "Mumbai",
"ifsc": "UTIV9089",
"accountno": 2646768
}JSON Arrays
A JSON array shops information inside a JSON file as a block enclosed in sq. brackets, [ ].
Right here is an instance of a JSON file that has JSON Array as its content material.
[
{
"numberrange": 5,
"name": "Dylan Hood",
"phone": "1-216-578-5381",
"email": "sollicitudin@aol.com",
"country": "Belgium",
"alphanumeric": "QKU41NZC5PB"
},
{
"numberrange": 7,
"name": "Jeremy Joyce",
"phone": "1-751-217-3163",
"email": "in.faucibus@aol.com",
"country": "Indonesia",
"alphanumeric": "YBO34KQQ8HO"
}
]Within the above instance, there’s a JSON array holding two objects inside it. The info inside sq. brackets [ ] is an Array and the info inside curly brackets { } are objects.
Named JSON Array
JSON permits naming the arrays. So, we will present names to the JSON array for straightforward recognition and readability. The next is an instance of a JSON file displaying the worker particulars in an array named “workers”.
{
"workers": [
{
"name": "John",
"email": "john@gmail.com",
"age": 26,
"designation": "QA"
},
{
"name": "Dennis",
"email": "dennis.c@gmail.com",
"age": 30,
"designation": "Developer"
},
{
"name": "Elizabeth",
"email": "elizb@gmail.com",
"age": 24,
"designation": "Secretary"
},
{
"name": "Steve",
"email": "s.deff@gmail.com",
"age": 29,
"designation": "Test Architect"
}
]
}Methods to Learn Json Information in Java Utilizing the Google Gson Library
JSON information are easy, straightforward, and light-weight, as we learn within the earlier part of the weblog in regards to the completely different file content material varieties a JSON file holds. Let’s now concentrate on tips on how to learn the JSON file utilizing the Google Gson library.
What Is Google Gson?
Gson, developed by Google, is a Java library that allows the conversion of Java objects to JSON format and can even parse JSON strings to create equal Java objects. It’s an open-source library obtainable on GitHub that’s vastly in style with 23.4k stars and 4.3k forks.
Getting Began
We might be making a Maven venture and including the next dependency within the pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<model>2.11.0</model>
</dependency>Moreover, we might be including the Lombok dependency that can permit us to create POJOs on runtime and keep away from writing boilerplate codes. We can even add the Hamcrest dependency that can assist us in assertions.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-all</artifactId>
<model>1.3</model>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<model>1.18.34</model>
<scope>supplied</scope>
</dependency>This completes the venture setup, let’s now delve into the code and be taught to learn the JSON information utilizing the Google Gson library.
Methods to Learn a JSON File That Has Solely a JSON Object
Let’s start with a easy JSON file that has a JSON object. The next file might be used within the demo and we might be printing the values within the console after studying the file.
- Filename: cardetails.json:
{
"carname": "Ferrari",
"makeyear": 2024,
"engine": "F1V12",
"estimatedprice": "450K USD"
}Let’s create a brand new Java class ReadJsonObject and add the next code to the primary technique.
public class ReadCarDetails {
public static void primary (String[] args) {
Gson gson = new Gson ();
attempt (Reader reader = new FileReader (System.getProperty ("person.dir") + "/src/take a look at/sources/cardetails.json")) {
CarDetails carDetails = gson.fromJson (reader, CarDetails.class);
System.out.println (carDetails);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error("Error studying JSON file");
}
}
}Code Walkthrough
We might be utilizing the Reader class of Java to learn the file cardetails.json that’s saved within the “src/take a look at/sources” folder. The System.getProperty(“person.dir”) will navigate to the working listing (i.e., the foundation folder of the venture) after which utilizing the trail “src/take a look at/sources/” we might be navigating to the precise file cardetails.json.
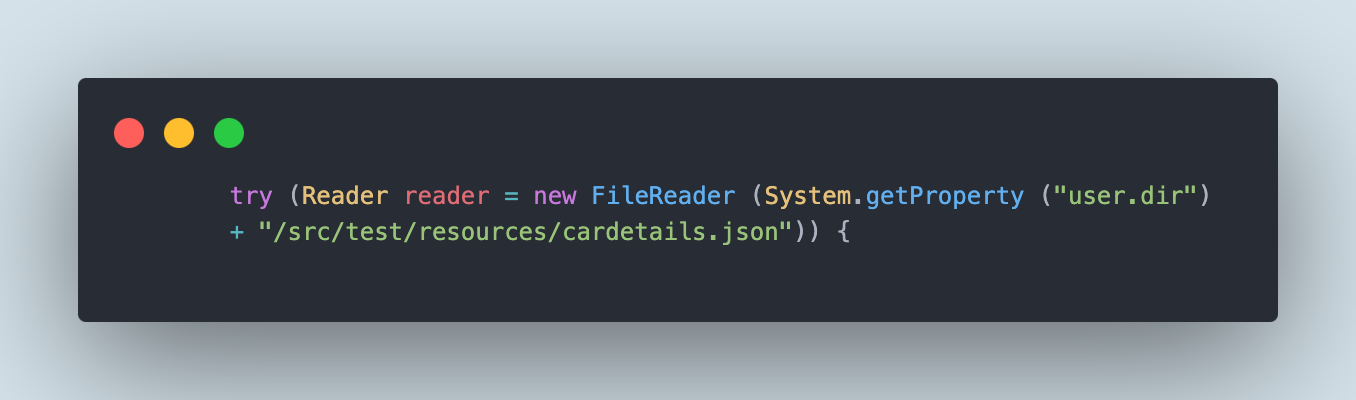
We might be utilizing the Attempt with sources assertion because it ensures that every useful resource is closed on the finish of the assertion. It auto closes the useful resource so we don’t need to deal with it particularly.
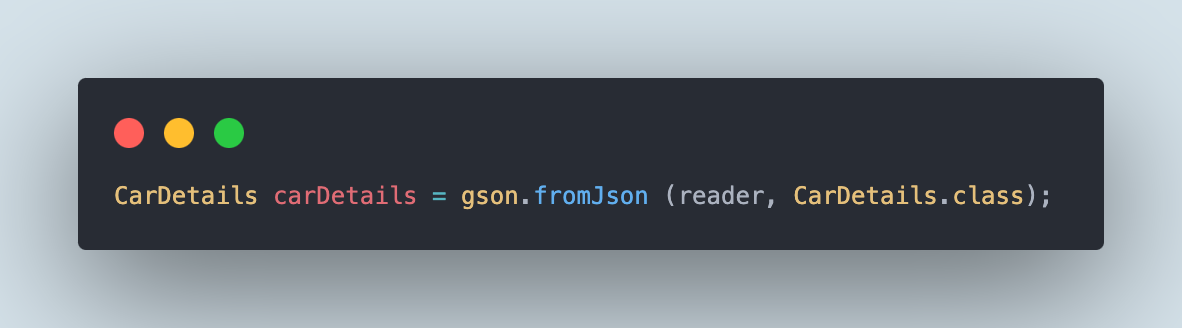
The fromJson() technique from the Gson class might be used to learn the JSON file. It accepts two parameters: the primary one is the JSON reader and the second is the POJO class.
The POJO class incorporates all of the corresponding key names of the file. A brand new class CarDetails.java has been created to deal with the POJO.
@ToString
@Getter
public class CarDetails {
non-public String carname;
non-public int makeyear;
non-public String engine;
non-public String estimatedprice;
}Discover that there are not any Getters and Setters on this POJO class. It’s as a result of we’re utilizing Lombok and have positioned the annotation @Getter over the category declaration. This @Getter annotation ensures that the Getter strategies might be created on runtime for additional use. Equally, the @ToString annotation will convert the thing to the string so we will view the precise string values within the output.
Lastly, we might be printing all of the values within the console after studying the JSON file.
Output
The next output of this system is printed within the console.
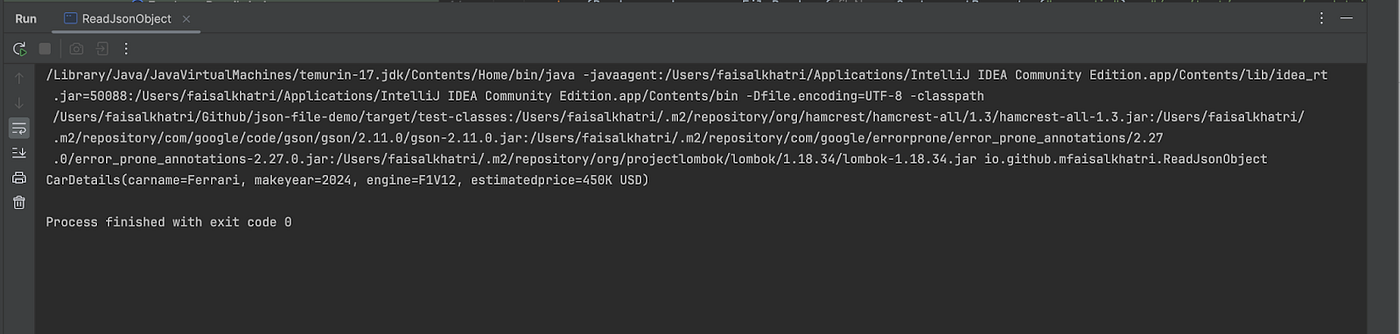
The file particulars with the important thing and its respective values are printed within the console appropriately as anticipated.
Methods to Learn a JSON File That Has JSON Arrays
A JSON file can maintain information in JSON Arrays that may have a number of JSON Objects. There are a number of approaches utilizing which the JSON file with JSON Arrays may be learn.
The next three approaches might be demonstrated for studying the JSON file with JSON Array:
- Studying the JSON Arrays utilizing the
TypeTokenclass of Gson library - Studying the JSON Arrays utilizing Java
Listing - Studying the JSON Arrays utilizing Java
Arrays
Studying the JSON Arrays Utilizing the TypeToken Class of Gson Library
Let’s take an instance JSON file holding the client particulars inside a JSON Array with a number of JSON objects.
- Filename: customerdetails.json:
[
{
"customerid": 5,
"name": "Dylan Hood",
"phone": "1-216-578-5381",
"email": "sollicitudin@aol.com",
"country": "Belgium",
"Coupon": true
},
{
"customerid": 7,
"name": "Jeremy Joyce",
"phone": "1-751-217-3163",
"email": "in.faucibus@aol.com",
"country": "Indonesia",
"Coupon": true
},
{
"customerid": 8,
"name": "Kyle Dominguez",
"phone": "(835) 147-8401",
"email": "pede.blandit@icloud.net",
"country": "Vietnam",
"Coupon": true
},
{
"customerid": 19,
"name": "Libby Nash",
"phone": "1-145-851-9979",
"email": "integer@outlook.com",
"country": "Spain",
"Coupon": false
},
{
"numberrange": 21,
"name": "Willow Graves",
"phone": "1-356-817-7211",
"email": "ipsum.suspendisse@outlook.edu",
"country": "Singapore",
"Coupon": false
}
]
A POJO class must be created that can assist in deserializing the JSON file and assist us in parsing and getting the values from the file.
@Getter
@ToString
public class CustomerDetails {
non-public int customerid;
non-public String title;
non-public String cellphone;
non-public String electronic mail;
non-public String nation;
non-public boolean coupon ;
}The Lombok library might be used right here because it removes the necessity to write the boilerplate code for the Getter strategies. With Lombok, we simply want to position the @Getter annotation over the POJO class.
Subsequent, we might write the code to learn the file by creating a brand new class ReadCustomerDetails.java.
public class ReadCustomerDetails {
public static void primary (String[] args) {
Gson gson = new Gson ();
attempt (
Reader reader = new FileReader (
System.getProperty ("person.dir") + "/src/take a look at/sources/customerdetails.json")) {
Kind listCustomerDetailsType = new TypeToken<Listing<CustomerDetails>> () {
}.getType ();
Listing<CustomerDetails> customerDetailsList = gson.fromJson (reader, listCustomerDetailsType);
System.out.println ("Printing all the client particulars from the file: " + customerDetailsList);
System.out.println (
"Printing the client particulars from the third Json Object from file: " + customerDetailsList.get (2));
System.out.println (
"Printing the title of the client from second Json Object: " + customerDetailsList.get (1)
.getName ());
System.out.println (
"Printing the e-mail of the client from third Json Object: " + customerDetailsList.get (2)
.getEmail ());
System.out.println (
"Printing the Coupon particulars of buyer from the third Json object: " + customerDetailsList.get (2)
.isCoupon ());
MatcherAssert.assertThat (customerDetailsList.get (3)
.getCountry (), equalTo ("Spain"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error ("Error studying JSON file");
}
}
}
Code Walkthrough
The Reader class of Java is used to learn the JSON file, “customerdetails.json,” which is saved within the “src/take a look at/sources/” folder.
The System.getProperty(“person.dir”) is used to retrieve the present working listing of the Java course of after which the relative path “src/take a look at/sources/customerdetails.json” is equipped.
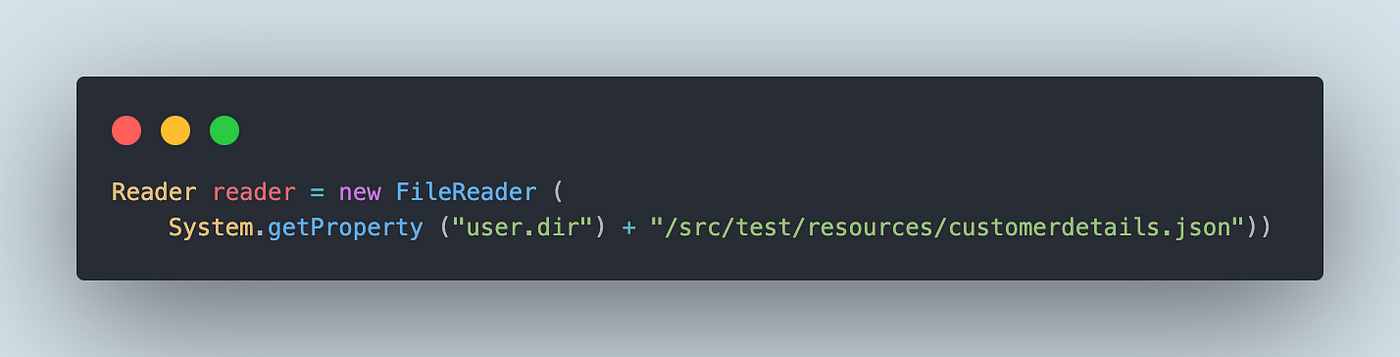
The reader object created within the first line is used additional to learn the JSON file’s content material.
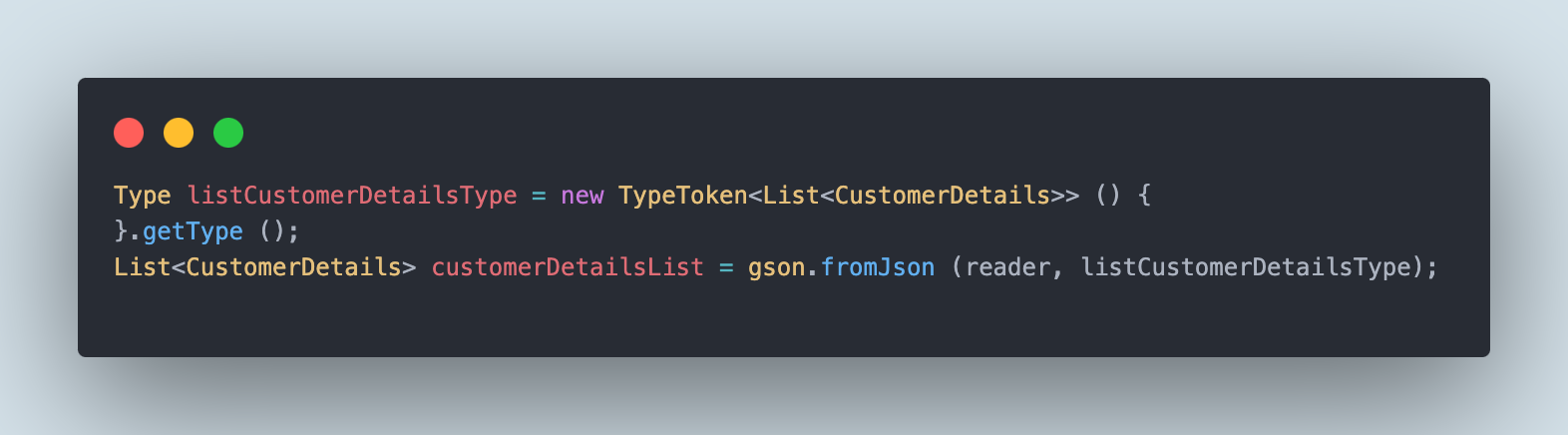
The Kind is a generic sort descriptor in Java that’s used for storing sort data at runtime. It’s particularly extra helpful whereas coping with complicated generic varieties. The TypeToken class from the Gson library is used for getting the generic sort data for Listing<CustomerDetails>.
The TypeToken is a helper class from Gson that’s used for changing JSON objects to Java and vice versa. The .getType() technique fetches the Kind object and gives data to Gson to appropriately deserialize JSON into Listing<CustomerDetails>.
Subsequent, the fromJson() technique of the Gson library is used to parse the JSON information into the Java object. It accepts two parameters: the primary one is the reader object that factors to the JSON information within the file and the second is the listCustomerDetailsType that gives the Kind data to Gson so it could actually deserialize the JSON into Listing<CustomerDetails>.
The customerDetailsList will maintain all the CustomerDetails objects. Every of the objects might be populated with information from the JSON file. The customerDetailsList can then be additional used for printing the JSON file values within the console.
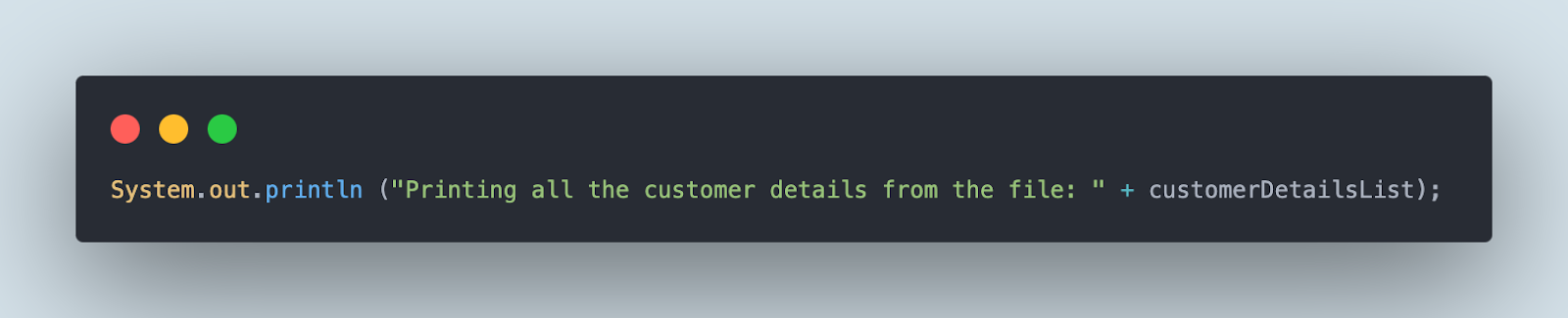
The next code will print all the client particulars within the console from all of the JSON objects within the file.
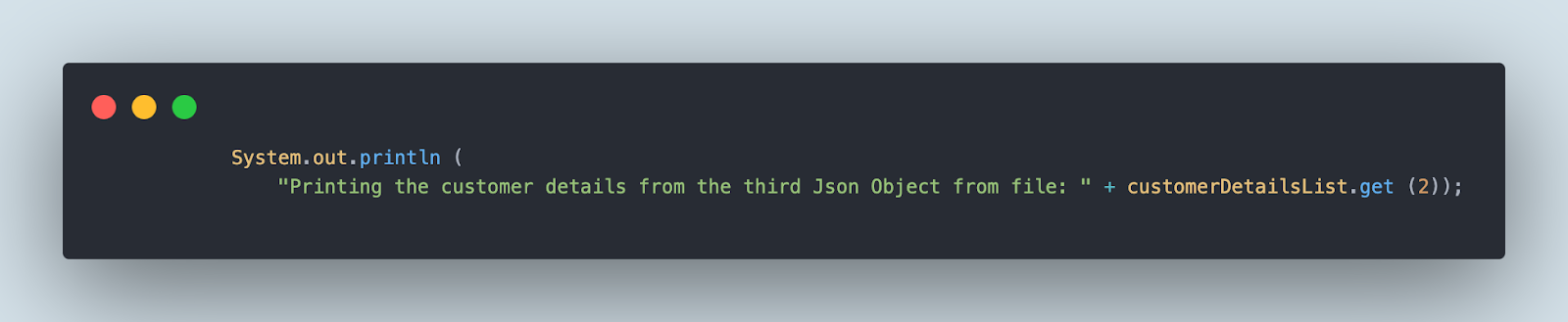
The next line of code will print all the client particulars within the console from the third JSON object within the file. That is completed by calling the get() technique with index “2”(since arrays begin with 0, therefore index 2 is used to get the third object).
All of the getter strategies are generated on runtime utilizing Lombok, therefore we simply must name the thing index utilizing the get() technique after which merely name the Getter technique to get the values from the file.
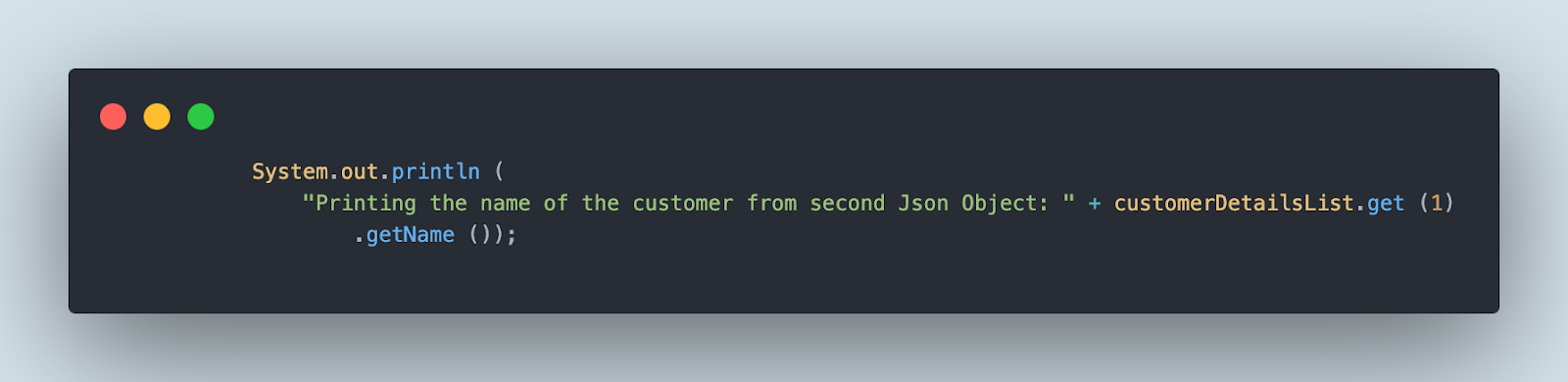
The next line of code will print the buyer title from the second JSON object within the file.
The next line of code will print the electronic mail and coupon particulars from the third JSON object within the file.
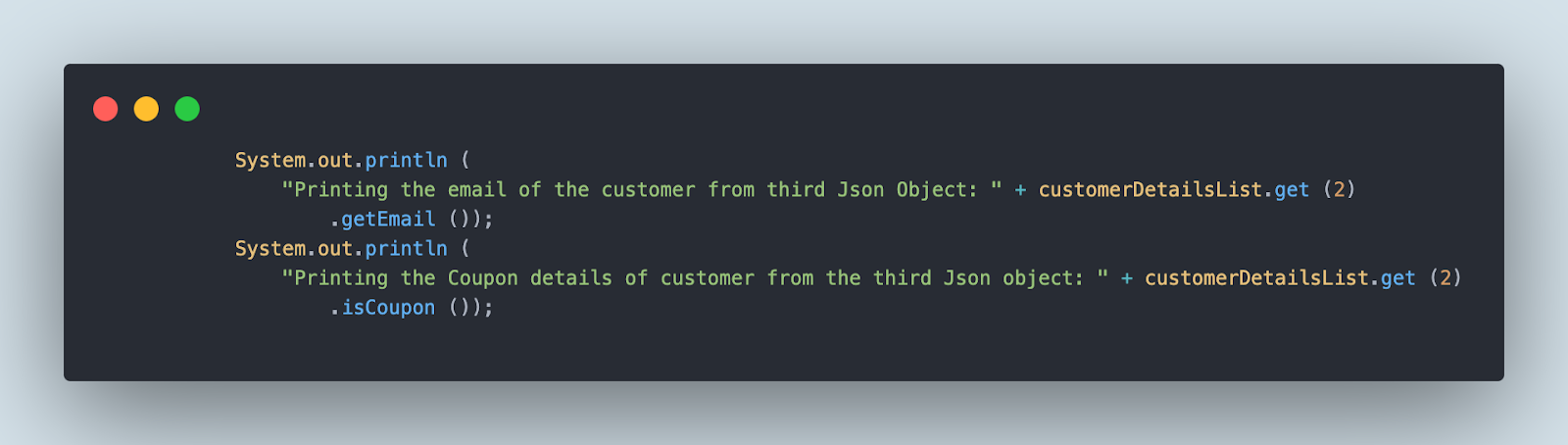
We might be performing an assertion to verify that the proper nation title is fetched from the file for the client from the fourth JSON object.
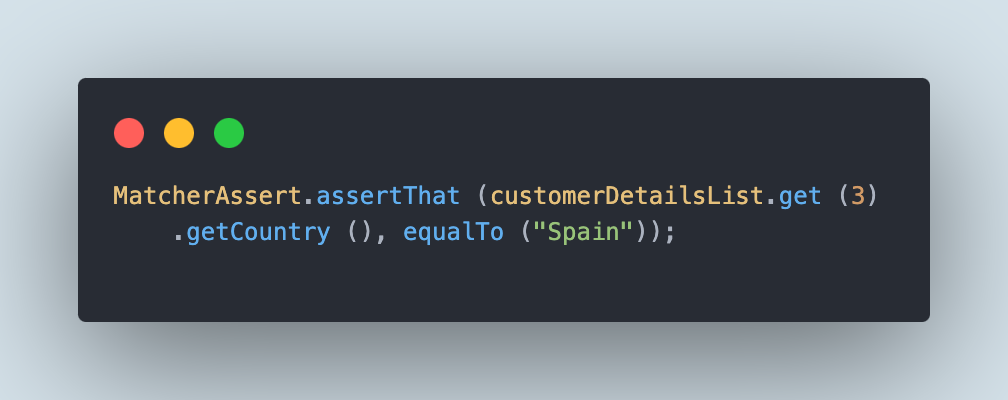
This assertion is written utilizing the assertThat() technique from the Hamcrest library.
Output
The next output of this system is printed within the console:
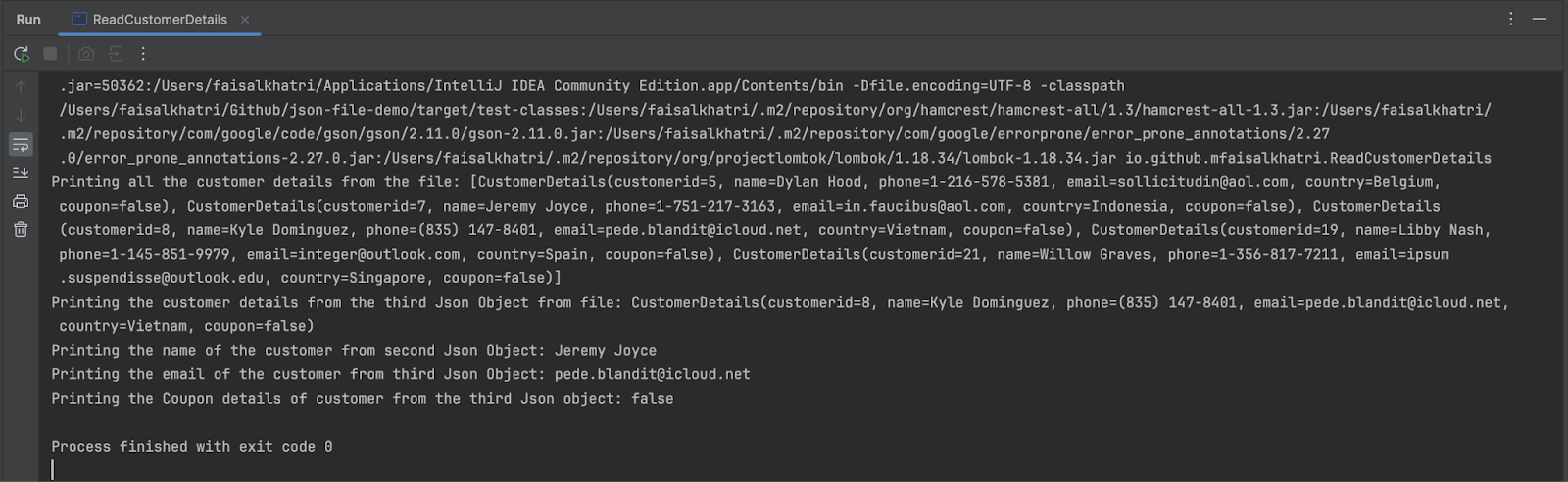
Within the first line, all the client particulars are printed. Subsequent, buyer particulars from the third JSON object are printed following which the title of the client from the second JSON object is printed.
Lastly, the e-mail and the coupon particulars from the third JSON object are printed.
Studying the JSON Arrays Utilizing Java Listing
Within the subsequent instance, we might be studying a JSON file holding the worker particulars in an array of a number of JSON objects. It is a JSON Array with the title “workers”.
- Filename: employeedetails.json
{
"workers": [
{
"name": "John",
"email": "john@gmail.com",
"age": 26,
"designation": "QA"
},
{
"name": "Dennis",
"email": "dennis.c@gmail.com",
"age": 30,
"designation": "Developer"
},
{
"name": "Elizabeth",
"email": "elizb@gmail.com",
"age": 24,
"designation": "Secretary"
},
{
"name": "Steve",
"email": "s.deff@gmail.com",
"age": 29,
"designation": "Test Architect"
}
]
}The POJO class , EmployeeDetails.java, will assist us in deserializing and parsing this JSON file.
@Getter
@ToString
public class EmployeeDetails {
non-public Listing<Workers> workers;
}The POJO is fairly easy: it holds the record of all the workers that might be dealt with utilizing one other POJO class , Workers.java.
@Getter
@ToString
public class Workers {
non-public String title;
non-public String electronic mail;
non-public int age;
non-public String designation;
}The Workers class has all of the fields obtainable within the JSON object. The following step is to create a brand new class ReadEmployeeDetailsAsList.java that can learn and parse the JSON file and print the output of the JSON file within the console.
public class ReadEmployeeDetailsAsList {
public static void primary (String[] args) {
Gson gson = new Gson ();
attempt (
Reader reader = new FileReader (
System.getProperty ("person.dir") + "/src/take a look at/sources/employeedetails.json")) {
EmployeeDetails employeeDetails = gson.fromJson (reader, EmployeeDetails.class);
System.out.println ("Printing all of the Worker Particulars: " + employeeDetails);
System.out.println (
"Printing the Worker Identify from the primary Json object: " + employeeDetails.getEmployees ()
.get (0)
.getName ());
System.out.println (
"Printing the Worker Designation from the second Json Object: " + employeeDetails.getEmployees ()
.get (1)
.getDesignation ());
MatcherAssert.assertThat (employeeDetails.getEmployees ()
.get (2)
.getEmail (), equalTo ("elizb@gmail.com"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error ("Error studying JSON file");
}
}
}
Code Walkthrough
An occasion of the Reader class is created implementing the FileReader class from Java that can learn the contents of the JSON file.
Subsequent, the fromJson() technique of the Gson library is used for parsing the JSON information into the Java object. There are two parameters equipped to this technique: the primary one is the reader object that factors to the JSON information within the file and the second is the particular goal sort for deserialization.
Gson will use the EmployeeDetails class to create an occasion of the stated class and populate it with the “workers” information from the JSON file.
The next line of code will print all the worker JSON objects from the file:
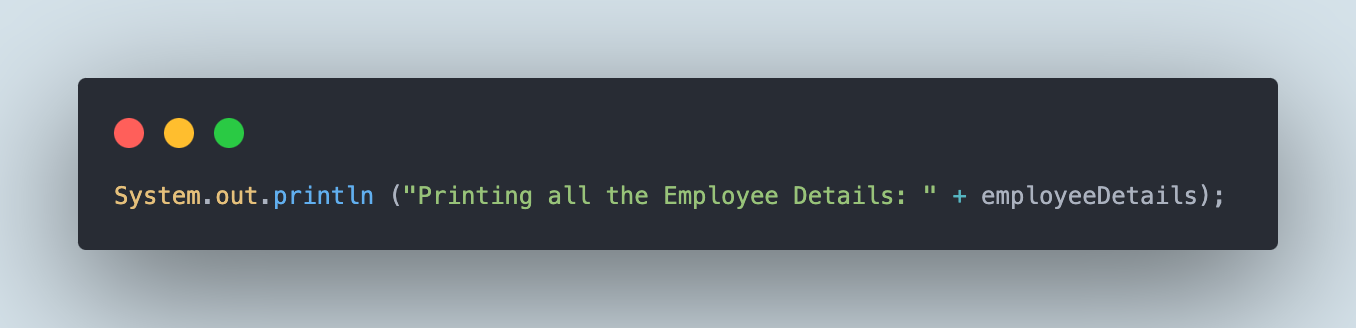
The next first print assertion will print the worker title from the primary JSON object whereas the second print assertion will print the worker designation from the second JSON object respectively.
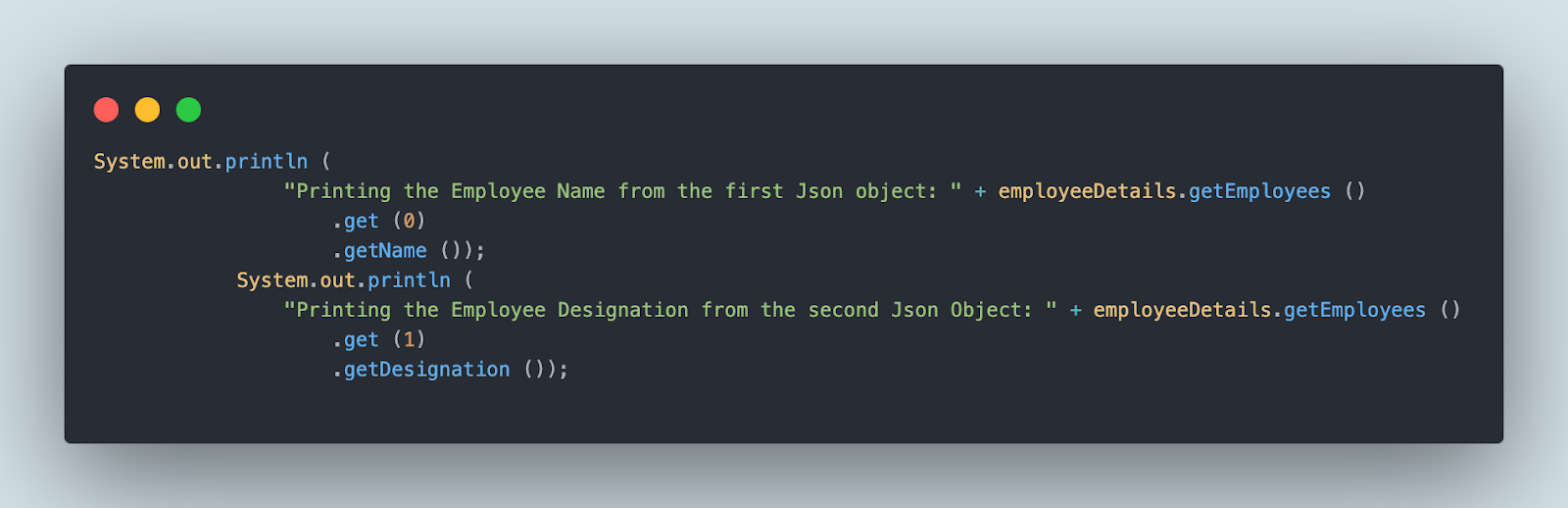
We are able to additionally carry out assertion of the values utilizing the Hamcrest library by fetching the worth from the JSON file and matching it with the anticipated worth as proven within the under screenshot.
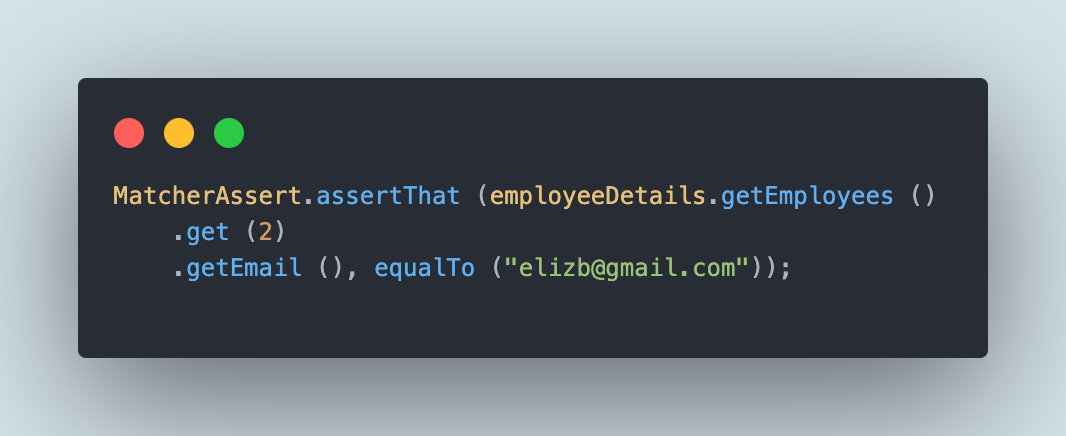
The above assert assertion will get the worker electronic mail from the third JSON object and verify that it equals to "elizb@gmail.com".
Output
The next is the output of the code printed within the console after the code is run.
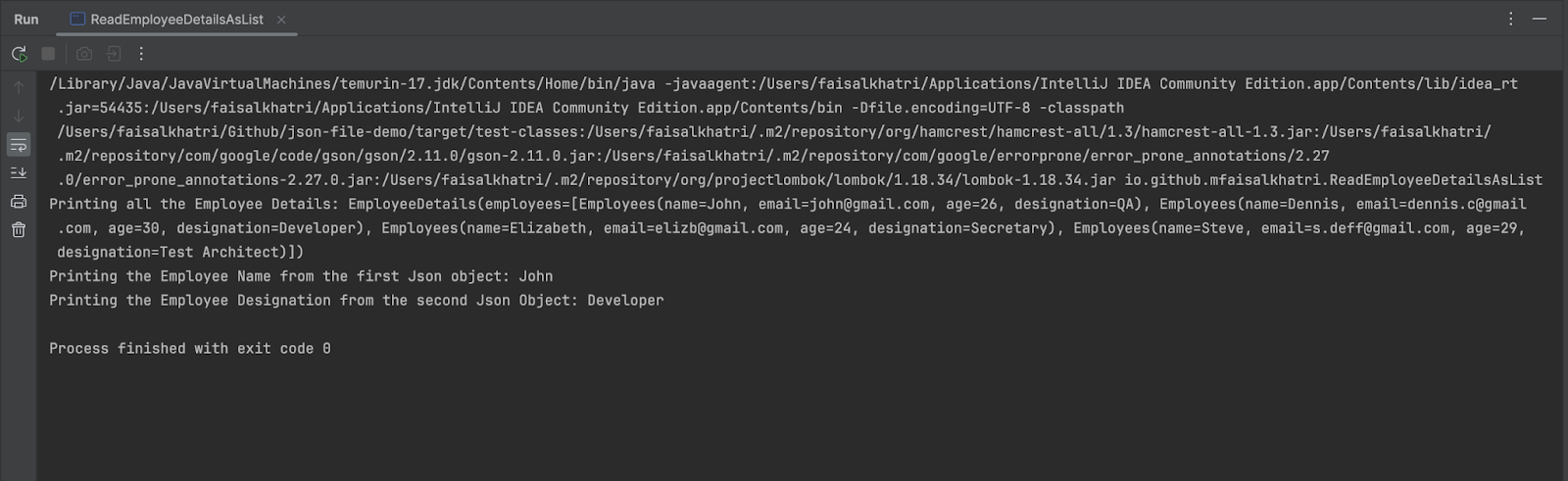
It may be seen within the console that each one the main points of the workers are printed first. Subsequent, the Worker Identify — “John” from the primary JSON object is printed efficiently. On the final line of the console, the Worker Designation = “Developer”, from the second JSON object is printed efficiently.
Studying the JSON Arrays Utilizing Java Arrays
One other solution to learn the JSON file with Arrays is utilizing the Java Arrays. On this part, we might be utilizing the identical EmployeeDetails.json file and studying it utilizing Java Arrays.
- Filename: employeedetails.json
{
"workers": [
{
"name": "John",
"email": "john@gmail.com",
"age": 26,
"designation": "QA"
},
{
"name": "Dennis",
"email": "dennis.c@gmail.com",
"age": 30,
"designation": "Developer"
},
{
"name": "Elizabeth",
"email": "elizb@gmail.com",
"age": 24,
"designation": "Secretary"
},
{
"name": "Steve",
"email": "s.deff@gmail.com",
"age": 29,
"designation": "Test Architect"
}
]
}
Let’s create a POJO class , EmployeeDetails.java, with a Java Array to parse the JSON file.
@Getter
@ToString
public class EmployeeDetailsAsArray {
non-public Workers[] workers;
}
We might be utilizing the prevailing POJO class Workers.java for mapping the JSON fields.
@Getter
@ToString
public class Workers {
non-public String title;
non-public String electronic mail;
non-public int age;
non-public String designation;
}
The following step is to create a brand new class ReadEmployeeDetailsAsList.java that can learn and parse the JSON file and print the output of the file within the console.
public class ReadEmployeeDetailsAsArray {
public static void primary (String[] args) {
Gson gson = new Gson ();
attempt (
Reader reader = new FileReader (
System.getProperty ("person.dir") + "/src/take a look at/sources/employeedetails.json")) {
EmployeeDetailsAsArray employeeDetails = gson.fromJson (reader, EmployeeDetailsAsArray.class);
System.out.println ("Printing all of the Worker Particulars: " + employeeDetails);
System.out.println (
"Printing the Worker Identify from the primary Json object: " + employeeDetails.getEmployees ().size);
System.out.println (employeeDetails.getEmployees ()[1].getName ());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error ("Error studying JSON file");
}
}
}Code Walkthrough
After studying the file utilizing the Reader class of Java, we might be utilizing the reader object and passing it as a parameter to the fromJson() technique of Gson class.
The second parameter of the fromJson() technique is the EmployeeDetailsAsArray.class that can create an occasion of the stated class and populate it with the “workers” information from the JSON file as an array.
The next line of code will print all of the JSON file values within the console.
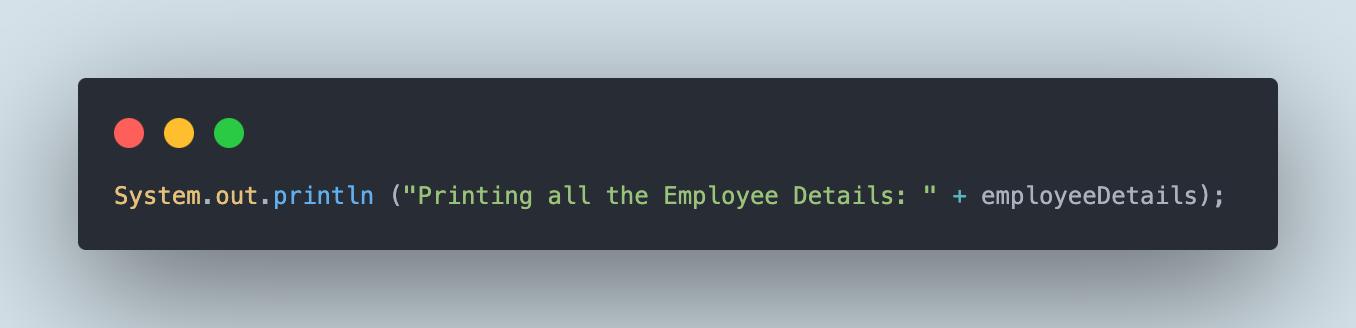
Subsequent, the next line of code will print the entire variety of JSON objects within the file.
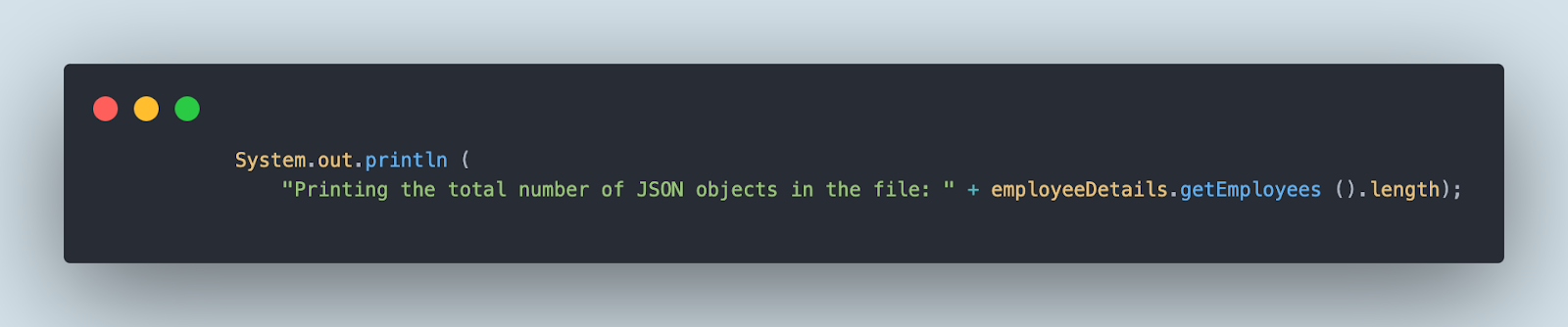
Now, to print the worker title from the second JSON object, we have to write the next line of code. It makes use of “[]” to get the required array object worth.
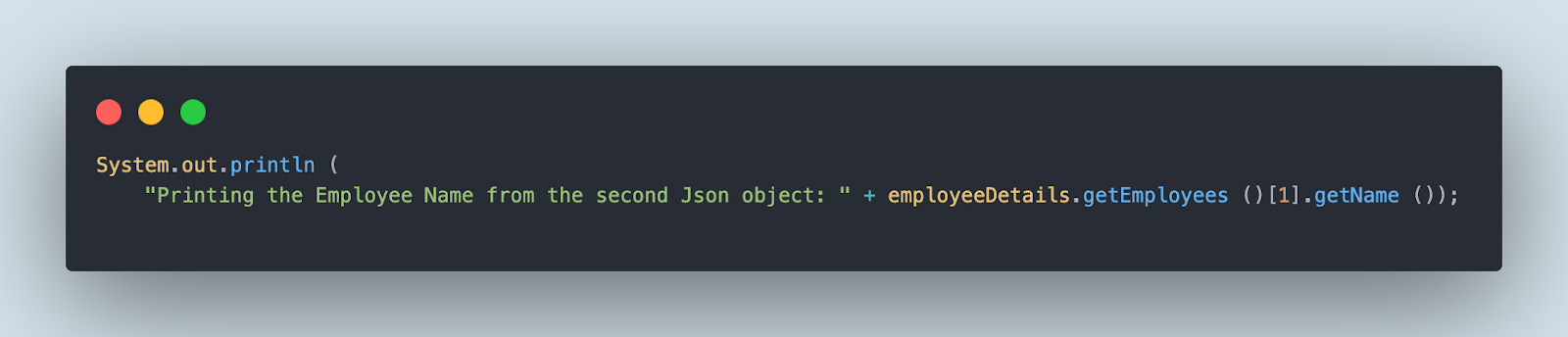
If we speak about readability, utilizing Java Listing or utilizing the TypeToken class to learn the file is way less complicated because it permits us to simply navigate to the JSON file objects. Nevertheless, utilizing Arrays, we should verify for the corresponding index to get the main points from the file which turns into a bit complicated.
Output
The next output is printed within the console after operating the code.
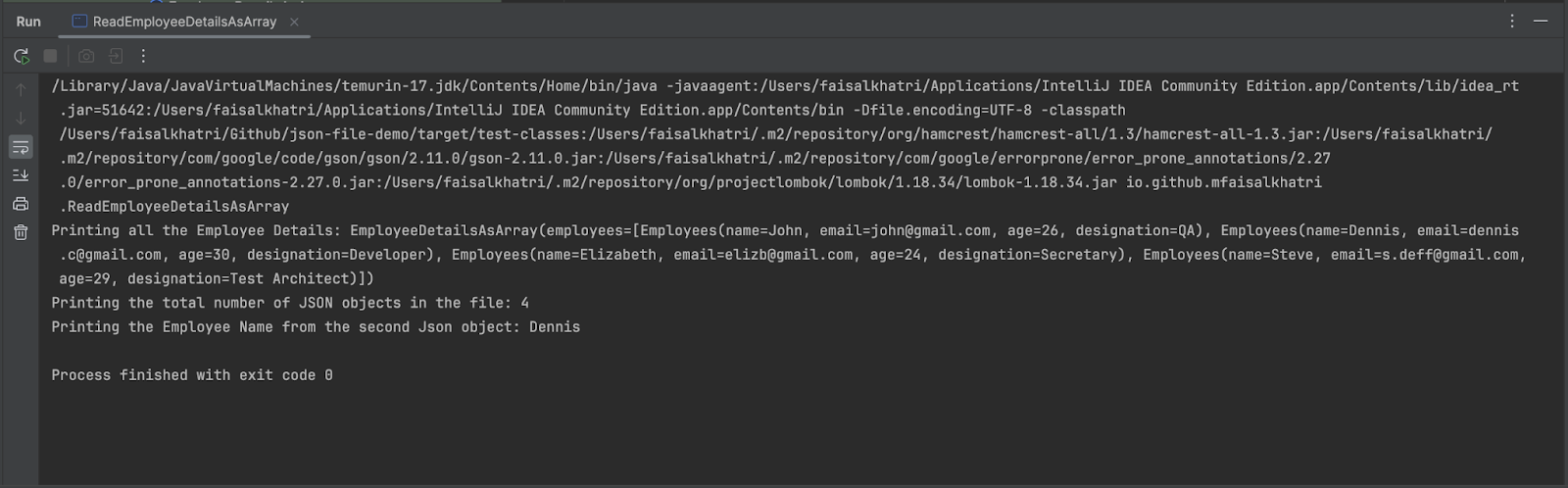
All the worker particulars are printed first, following the entire variety of JSON objects within the file, and eventually the worker title “Dennis” from the second JSON object.
Methods to Learn a JSON File That Has a JSON Object Inside a JSON Object
A JSON file can even have JSON objects which have one other JSON object inside it. Let’s take into account one such instance of a file, passengerdata.json under:
- Filename : passengerdata.json
{
"passengerdetails": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
"activeTraveller": true,
"origin": "Paris",
"destination": "Frankfurt",
"ticketdetails": {
"airlines": "Saudi Airlines",
"pnr": "PFJF45G",
"date": "29/10/2024",
"ticketamt": 45000
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Richard Dave",
"activeTraveller": true,
"origin": "Mumbai",
"destination": "Dubai",
"ticketdetails": {
"airlines": "Emirates",
"pnr": "PCG78Y",
"date": "31/10/2024",
"ticketamt": 26000
}
}
]
}
The passengerdata.json file has a number of objects of passenger particulars. Every Passenger element has an object of “ticket particulars” that has a number of fields in it.
With a purpose to learn this file, we might want to create three POJO courses. The primary POJO class might be for parsing the primary JSON Array that holds the “passengerdata”.
We might be utilizing Java Listing to parse the JSON arrays.
@Getter
@ToString
public class PassengerData {
non-public Listing<PassengerDetails> passengerdetails;
}The second POJO might be for parsing the “passengerdetails” and studying all its fields.
@Getter
@ToString
public class PassengerDetails {
non-public int id;
non-public String title;
non-public boolean activeTraveller;
non-public String origin;
non-public String vacation spot;
non-public TicketDetails ticketdetails;
}Observe: The title of the category and the title of the JSON Array needs to be the identical. In our case, the title of the JSON array is “
passengerdetails” therefore the POJO class is known as as “PassengerDetails”.
An essential level to notice on this class is that, for the reason that “ticketdetails” object is inside each object of the “passengerdetails”, therefore we can even place the TicketDetails POJO class contained in the PassengerDetails class.
The third POJO might be used for parsing the “ticketdetails” object and studying its fields.
@Getter
@ToString
public class TicketDetails {
non-public String airways;
non-public String pnr;
non-public String date;
non-public int ticketamt;
}After creating the POJO courses, we will transfer straight to writing the precise code for parsing and studying the contents of the “passengerdata.json” file.
Let’s create a brand new Java class, ReadPassengerData.json.
public class ReadPassengerData {
public static void primary (String[] args) {
Gson gson = new Gson ();
attempt (
Reader reader = new FileReader (
System.getProperty ("person.dir") + "/src/take a look at/sources/passengerdata.json")) {
PassengerData passengerData = gson.fromJson (reader, PassengerData.class);
System.out.println ("Printing all of the Passenger Information: " + passengerData);
System.out.println (
"Printing the Passenger Identify from the primary Json object: " + passengerData.getPassengerdetails ()
.get (0)
.getName ());
System.out.println (
"Printing the Ticket Particulars of the primary Json object: " + passengerData.getPassengerdetails ()
.get (0)
.getTicketdetails ());
MatcherAssert.assertThat (passengerData.getPassengerdetails ()
.get (1)
.getDestination (), equalTo ("Dubai"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error ("Error studying JSON file");
}
}
}
Code Walkthrough
The strategy to studying the file stays the identical as we realized by this weblog within the earlier sections. We might be calling the fromJson() technique of the Gson library the place the reader object, an object of the Reader class of Java is equipped after studying the JSON file.
Within the second parameter, the PassengerData.class object, is equipped that can create an occasion of the stated class and populate it with the “passengerdetails” information from the JSON file.
We might be printing the main points within the console by writing the code utilizing Java print statements. The next print assertion will print all of the JSON file information within the console.
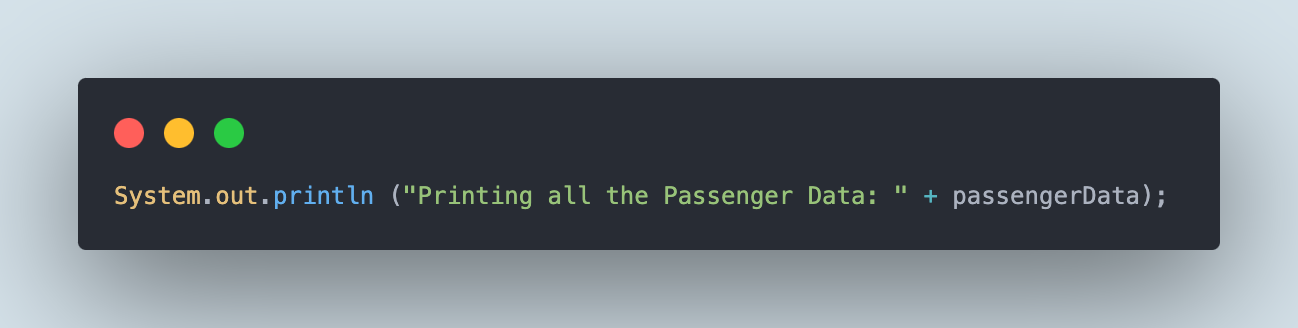
The next print assertion will print the passenger title from the primary JSON object.
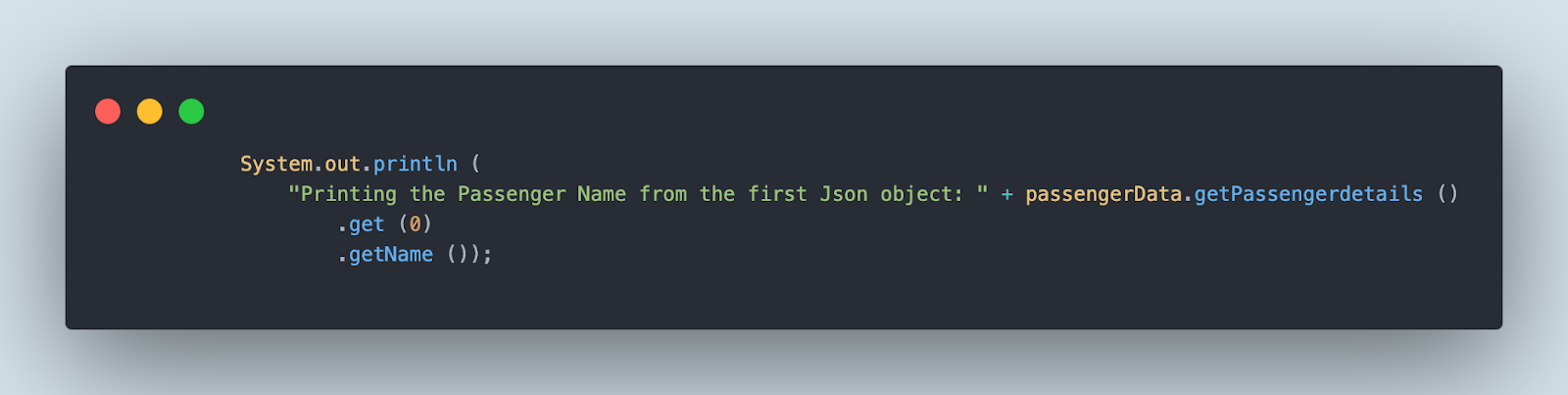
The next print assertion will verify that the vacation spot of the second passenger within the ticket particulars is “Dubai”.
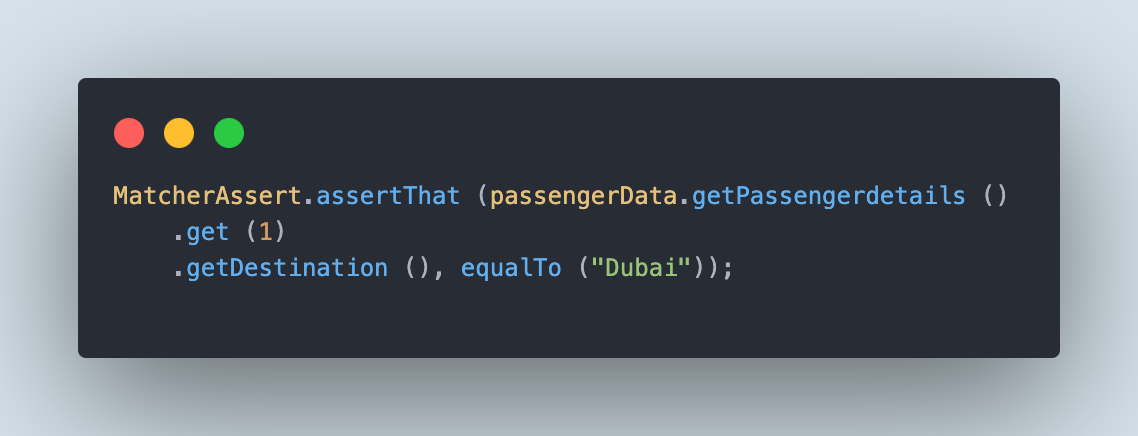
Likewise, we will use the occasion of the PassengerData class and skim the opposite particulars within the JSON file.
Output
Let’s execute the code and verify for the main points printed within the console.
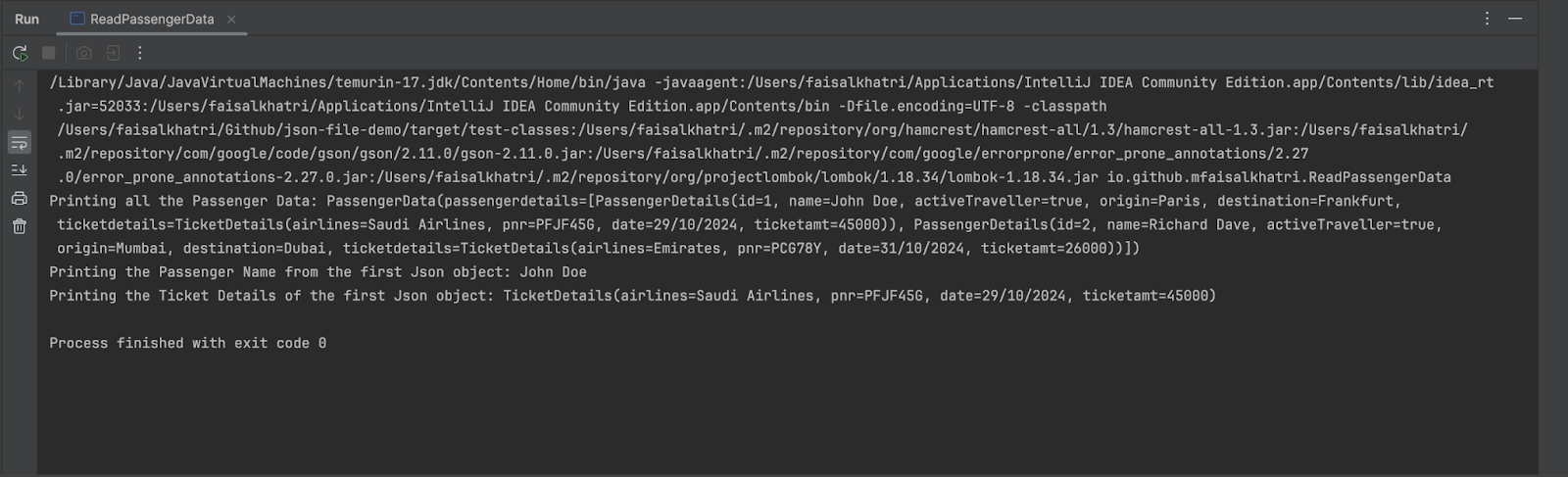
Within the first line, all of the passenger particulars from the JSON file are printed together with the ticket particulars. Within the second line, the passenger title, i.e., “John Doe”, from the primary JSON object is printed.
Within the final line, all the main points of the ticket are printed for the primary passenger. Lastly, because the assertion handed for checking the vacation spot of the second passenger, the execution didn’t throw any exception.
Abstract
The Google Gson library permits us to parse and skim the JSON file simply. This library turns out to be useful in case we need to arrange configurations within the take a look at automation/improvement initiatives utilizing the JSON file. Gson is a really light-weight and helpful library that permits us to simply learn the file with minimal code.
I’ve used this library in my take a look at automation initiatives for studying the take a look at framework configurations for Internet, Cellular, and API testing. I hope this tutorial weblog gave a good concept about utilizing Gson to parse and skim the completely different JSON file contents with completely different approaches.
Blissful testing!









